

Cosmetics
Personal Care Products
Household Cleaning Products
Packaging and Materials
Pharmaceuticals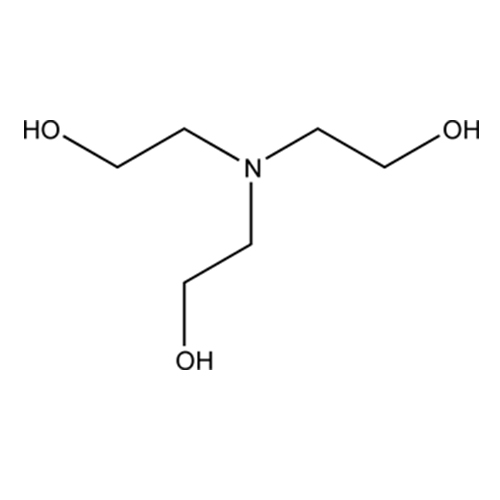
Triethanolamine, often abbreviated as TEA, is a viscous organic compound that is both a tertiary amine and a triol. Triethanolamine is a strongly alkaline substance used as surfactant, pH adjusting chemical, fragrance ingredient, and emulsifying agent.
Treithanolamine is used in a variety of cosmetic and personal care products, including eyeliners, mascara, eye shadows, blushers, make-up bases and foundations, as well as in fragrances, hair care products, hair dyes, wave sets, shaving products, sunscreens, and skin care and skin cleansing products. Triethanolamine is FDA approved as an indirect food additive (aka it can be used in packaging) and CIR approved with concentration limits. The CIR determined that Triethanolamine was "safe for use in cosmetics and personal care products designed for discontinuous, brief use followed by thorough rinsing from the surface of the skin. In products intended for prolonged contact with the skin, the concentration of Triethanolamine should not exceed 5%." Triethanolamine's production and use as chemical intermediate in the manufacture of surfactants, personal care products, detergents, and corrosion inhibitors, especially in coolants for automotive engines and additives for lubricating fluids, for cutting oils and for milling cement may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams.
According to Cosmetic Ingredient Review, Association of Occupational and Environmental Clinics, and the U.S. National Library of Medicine, there is strong evidence that Triethanolamine is a human skin, immune system and respiratory toxicant. One or more animal studies show sense organ effects at very low doses, especially when used around the mouth, eyes and lips, and one or more in vitro tests on mammalian cells show positive mutation results. It has been shown to cause bladder and liver cancer, as well as changes in testicles. According to OrganicConsumers.org, Triethanolamine can cause allergic reactions including eye problems, dryness of hair and skin, and could be toxic if absorbed into the body over a long period of time. It can cause itching, burning, scaling, hives, and blistering of skin, all symptoms which may increase with higher concentrations (The Green Beauty Guide). Triethanolamine "should not be used in products containing N-nitrosating agents to prevent the formation of possibly carcinogenic nitrosamines."
Also seen as 2,2',2"-NITRILOTRIS [ETHANOL] ; 2,2',2''-NITRILOTRIETHANOL; ETHANOL, 2,2 ,2 NITRILOTRIS; ETHANOL, 2,2',2"-NITRILOTRIS-; TEA; TROLAMINE; 2,2',2''-NITRILOTRIETHANOL; ALKANOLAMINE 244; DALTOGEN; NITRILO-2,2',2''-TRIETHANOL; STEROLAMIDE
Reference: http://bit.ly/1PTZ9L4
See Nitrosating Agents (http://bit.ly/2bcjxHE)
No articles were found